What is a current transformer and How does a current transformer work?
A current transformer (CT) is a device to measure electric current. The purpose of a current transformer is to transform high currents into lower, more manageable levels that can be easily measured and monitored through measuring instruments. It consists of a primary winding, which is connected in series with the current-carrying conductor, and a secondary winding that is connected to a measuring or monitoring instrument. A hand held clamp-meter is also a C.T which measures current flowing in wires. A typical current transformer used in a substation looks like this:
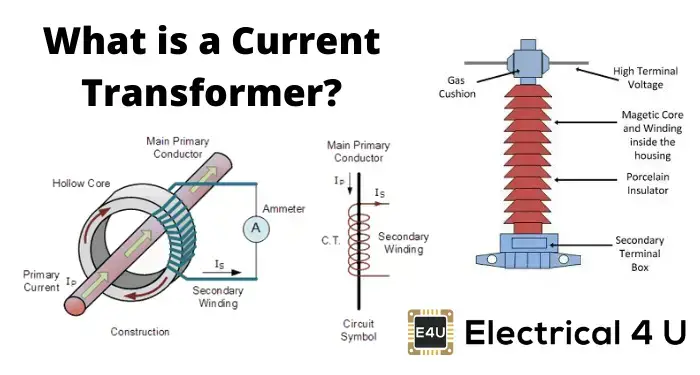
(P.C-electrical4u.com)
The primary current is the current that needs to be measured or monitored, and it is typically high in magnitude. The CT reduces (step down) this high current to a safe and measurable level in the secondary circuit, usually a standard current value such as 5 amperes (A) or 1 ampere (A). The secondary current is then used for various purposes, such as metering, protection, and control.
The number of turns in the primary and secondary windings determines the turns ratio and the magnitude of the secondary current with respect to the primary current. A current transformer (CT) works based on the principle of electromagnetic induction just like a normal transformer. When an electric current flows through the primary winding of a CT, it generates a magnetic field around the primary winding. This magnetic field induces a proportionate current in the secondary winding of the CT.
Current transformers used in industry & Substations are mostly of primary current/1A ratio or primary current/5A ratio. For e.g 1200/1 ,600/1 ,300/5 etc. Suppose we have a C.T of ratio 300/1 then what does it mean? It means that when primary current is 300A then secondary current will be 1A and if current becomes half to 150A, Secondary current will also become half i.e 0.5A. Industrial C.Ts have many cores and these cores are used for different purpose.
Why we need multiple cores in a C.T?
Cores are basically parallels connection/ tappings from secondary side. Suppose If a C.T has three cores of ratio 300/1 , then one core can be used for metering, second for main protection and third for backup protection. But why we need these many cores in the first place?
Suppose if both Main protection and backup protection circuit is connected with one core of the C.T and if some fault occurs in that core, then both protection circuits will become faulty at once thus endangering the equipment protection . Multiple core arrangement is used for making the secondary circuits simplified so that if problem/fault occurs in one secondary circuit, it doesn’t affect the other circuit as separate and dedicated wires from different cores are used. Other benefit is that sometimes the core of C.T also saturates due to excessive currents & aging , if there are multiple cores available in a C.T, spare cores can be used in case of saturation of a particular core.
Testing and commissioning :
Here are some common tests conducted on current transformers:
- Ratio Test: This test determines if the turns ratio of the current transformer is within the specified range. A known current is applied to the primary winding, and the resulting secondary current is measured. By comparing the primary and secondary currents, the turns ratio can be calculated.
- Polarity Test: The polarity test checks the direction of the current flow in the secondary winding relative to the primary winding. It ensures that the current transformer is correctly connected in the system, and the polarities of primary and secondary currents match.
- Excitation Test: This test evaluates the performance of the current transformer under different levels of magnetizing current. It measures the secondary current produced when a known excitation current is applied to the primary winding. This test helps determine the accuracy and linearity of the current transformer.
- Accuracy Class Test: Current transformers have specified accuracy classes that define their accuracy limits. The accuracy class test involves comparing the actual secondary current with the rated secondary current at different primary currents. This test ensures that the current transformer meets the required accuracy standards.
- Burden Test: The burden test assesses the performance of the current transformer when connected to its intended load, such as protective relays or measuring instruments. It verifies that the current transformer can handle the specified burden without significant errors or distortions.
- Saturation Test: Saturation occurs when the core of the current transformer becomes magnetically saturated due to excessive current. The saturation test checks the performance of the current transformer under high current conditions to ensure it operates within acceptable limits.
- IR test: IR values of Primary to earth ,between all Cores to earth and among the cores are also taken to ensure healthiness of insulation.
- Tan delta test: Tan-delta point is provided in C.T of 132KV and above voltage level for conducting tan-delta test. This test is done with the help of tan delta kit and the process has been explained here.
A name plate of C.T may look like this. PS denotes the protection cores and class where 0.2 is mentioned is metering core. From protection cores , connection is made for Main relays and backup relay and from metering core connection is made to the energy meters.
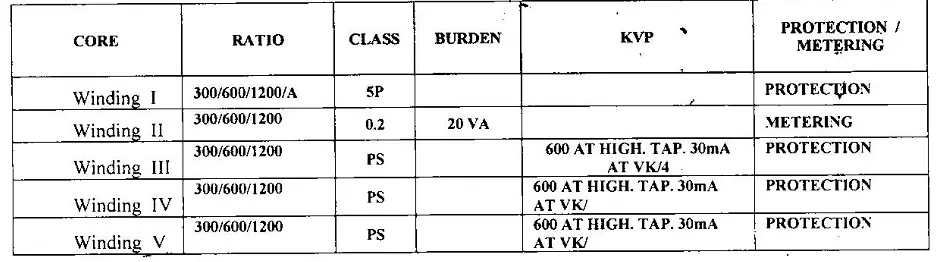
5P, 10P and 15P are the maximum composite error corresponding to accuracy limit primary current.
Following IR readings for a five core C.T is taken:
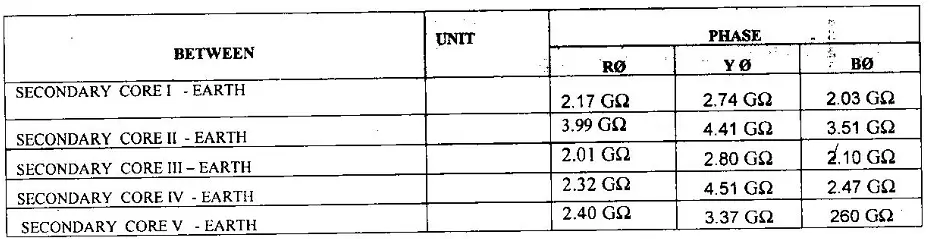
Ratio test is conducted as follows:
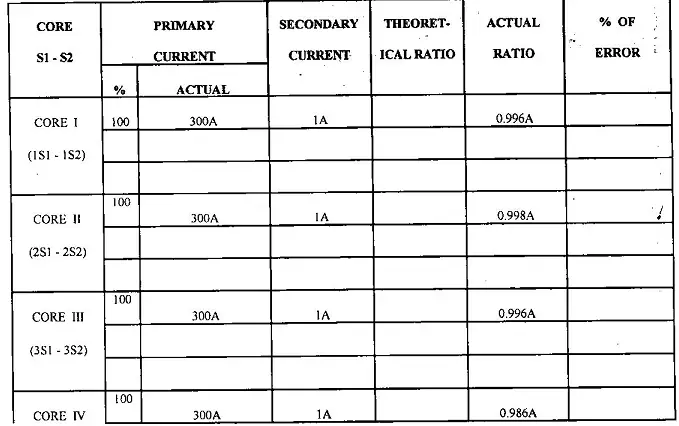
After getting satisfactory test results , we can successfully commission a C.T.
You may watch this for more info:
Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) on current transformers:
What is a Current Transformer (CT)?
A Current Transformer (CT) is a device designed to measure alternating current (AC) by producing a current in its secondary winding that is proportional to the current flowing in its primary winding.
How does a Current Transformer work?
A CT works on the principle of electromagnetic induction. It consists of a primary winding, which is connected in series with the current to be measured, and a secondary winding. The secondary winding produces a reduced current proportional to the primary current.
What are the key components of a Current Transformer?
The main components include the primary winding, secondary winding, magnetic core, and sometimes a burden resistor. The magnetic core enhances the transformer’s performance by concentrating the magnetic field.
What is the purpose of a Burden Resistor in a CT?
A burden resistor is connected across the secondary winding of a CT to provide a load for the transformer. It ensures that the secondary current is accurately proportional to the primary current and allows for measurement or protection devices to be connected.
What are the typical applications of Current Transformers?
CTs are commonly used in electrical power systems for metering, protection, and control purposes. They are essential in measuring current for billing, monitoring power quality, and providing inputs to protective relays.
How is the accuracy of a Current Transformer defined?
CT accuracy is typically expressed as a percentage, indicating the maximum allowable error under specified conditions. Classes such as 0.2, 0.5, 1.0, and 3.0 are commonly used to denote accuracy levels.
Can a Current Transformer be used for direct current (DC) measurements?
Generally, CTs are designed for AC measurements. Attempting to use them for DC measurements may result in inaccuracies or damage to the transformer.
What is the difference between a Current Transformer and a Voltage Transformer (Potential Transformer)?
While both transformers operate on similar principles, a Current Transformer measures current, whereas a Voltage Transformer measures voltage. They serve different purposes in power systems.
How is a Current Transformer connected in a circuit?
The primary winding is connected in series with the conductor carrying the current to be measured. The secondary winding is connected to the measuring or protective devices.
What precautions should be taken when installing a Current Transformer?
Proper installation is crucial. Ensure correct polarity, adequate insulation, and compliance with safety standards. Also, avoid leaving the secondary winding open-circuited to prevent damage.