A control system consisting of interconnected components is designed to achieve a desired purpose .Modern control engineering practice includes the use of control design strategies for improving manufacturing processes, the efficiency of energy use, advanced automobile control, including rapid transit, among others.
History of Control Systems :
Few examples of earlier control system are :
Liquid-Level Control :The level of water in the measuring container could be used to tell time
Steam Pressure and Temperature Controls :If the upward pressure from the boiler exceeded the weight, steam was released, and the pressure decreased. If it did not exceed the weight, the valve did not open, and the pressure inside the boiler increased.
Basic components of a control system
- Plant: The portion of a system that is to be controlled or regulated is called a plant or process. It is a unit where actual processing is performed and if we observe in the above figure, the input of the plant is the controlled signal generated by a controller. A plant performs necessary actions on a controlled system and produces the desired output.
- Feedback: It is a controlled action in which the output is sampled and a proportional signal is given to the input for automatic correction of any changes in the desired output. The output is given as feedback to the input for correction i.e. information about the output is given to input for correcting the changes in output due to disturbances. The feedback signal is fed to the error detector. Negative feedback is preferred as it results in better stability and accuracy. The other disturbance signals are rejected.
- Error detector: The function of the error detector is to compare the reference input with the feedback signal. It produces an error signal which is a difference of two inputs which are a reference signal and a feedback signal. The error signal is fed to the controller for necessary controlled action. This error signal is used to correct the output if there is a deviation from the desired value.
- Controller: the element of a system within itself or external to the system which controls the plant is called as a controller. The error signal will be a weak signal and so it has to be amplified and then modified for better control action. In most of the systems, the controller itself amplifies the error signal and integrates or differentiates to generate a control signal. An amplifier is used to amplify the error signals and the controller modifies the error signal.
Open-loop systems:
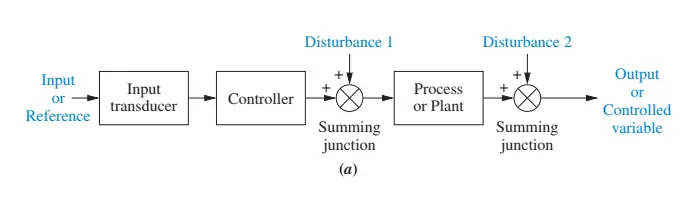
A control system in which the control action is totally independent of the output of the system then it is called an open-loop control system. A system that is not capable of correcting the changes in the output by itself is called as an open-loop system. For example, toasters are open-loop systems. The controlled variable (output) of a toaster is the color of the toast. The device is designed with the assumption that the toast will be darker the longer it is subjected to heat and the toaster does not correct itself for bread thickness, conditions etc.
Closed-Loop (Feedback Control) Systems
It is a type of control system where the output is continuously monitored and compared to the desired set point or reference. Based on this comparison, the system automatically adjusts its input to minimize the error and bring the output closer to the desired value.
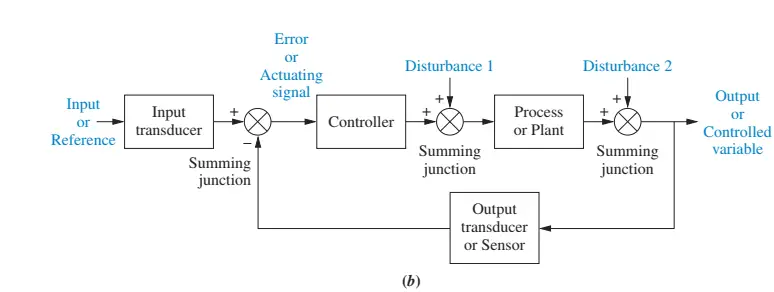
The first summing junction algebraically adds the signal from the input to the signal from the output, which arrives via the feedback path, the return path from the output to the summing junction.Closed-loop systems, then, have the obvious advantage of greater accuracy than open-loop systems. They are less sensitive to noise, disturbances, and changes in the environment.
An example of a closed-loop system is a thermostat-controlled heating system:
Feedback: The thermostat continuously monitors the temperature and adjusts the heating as needed.
Set Point: Desired room temperature (e.g., 22°C).
Sensor: Temperature sensor that measures the current room temperature.
Controller: The thermostat that compares the measured temperature to the desired set point.
Actuator: The heater, which turns on or off based on commands from the thermostat.
Process: The heating of the room.
Modern control system
1. Smart Grid
- Description: A smart grid is an electrical grid enhanced with digital communication and automation. It optimizes the generation, distribution, and consumption of electricity using real-time data from various sources.
- Control System Components: Advanced metering infrastructure (AMI), intelligent electronic devices (IEDs), remote terminal units (RTUs), and supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems.
- Functionality: It improves the efficiency of electricity distribution, integrates renewable energy sources, and provides real-time monitoring of power demand and supply.
2. Autonomous Vehicles
- Description: Autonomous or self-driving vehicles use control systems to manage navigation, braking, acceleration, and obstacle detection.
- Control System Components: Sensors (LiDAR, radar, cameras), artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning algorithms, and controllers.
- Functionality: These systems process data from sensors and make real-time decisions for safe driving without human intervention.
3. Industrial Robotics
- Description: Modern industrial robots are used for manufacturing, assembly, and precision tasks in factories.
- Control System Components: Programmable logic controllers (PLCs), feedback systems, servo motors, and motion controllers.
- Functionality: Robots use feedback loops to adjust movements and operations in real-time, ensuring precision, speed, and adaptability in various tasks such as welding, painting, and assembling.
4. HVAC Control Systems
Functionality: HVAC systems adjust heating and cooling based on real-time conditions, providing energy efficiency and comfort in commercial and residential buildings.
Description: Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems in modern buildings use control systems to optimize indoor temperature and air quality.
Control System Components: Sensors, thermostats, dampers, fans, and central controllers.