Before we explain Star to Delta transformation and Delta to Star transformation, let us first understand these connections separately:
Contents
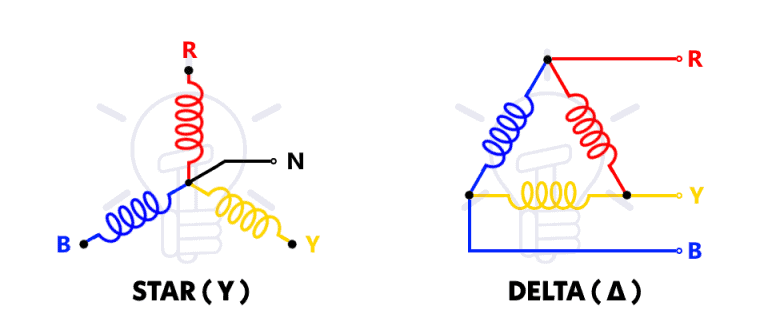
Star Connection (Y Connection)
Star connection is in shape of Y, therefore it is also called Y connection. In a star connection, three windings or terminals of the three-phase system are connected together at a common point known as the neutral point or star point.
- The three remaining terminals are then taken out as the output terminals.
- Symbolically, it resembles the shape of a star, hence the name.
- In a star-connected system, each load impedance is connected between one phase and the neutral, making it suitable for systems where a neutral connection is required.
- The line voltage VL in a star connection is equal to the phase voltage Vph.
Delta Connection (Δ Connection)
- In a delta connection, the end of each phase winding is connected to the start of the next winding to form a closed loop or triangle.
- The load is connected between each pair of phases.
- Symbolically, it resembles the Greek letter delta (Δ).
- In a delta-connected system, each load impedance is connected between two phases, and there’s no neutral connection by default.
- The line voltage (VL) in a delta connection is Sqrt 3 times the phase voltage (Vph).
Conversion formula
The conversion involves transforming a circuit from one configuration (star or delta) to the other while maintaining equivalent electrical characteristics.
Delta to Star transformation:
ZA,ZB,ZC are Star Impedance values and Z1,Z2 and Z3 are delta impedance values
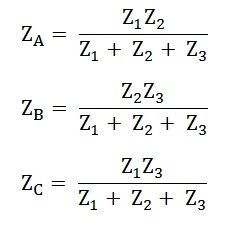
Star to Delta transformation:
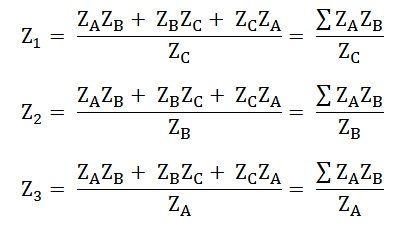
Key Differences:
Neutral Connection:
- A star connection inherently provides a neutral connection, which can be useful for systems requiring a neutral wire.
- A delta connection does not provide a neutral connection by default.
Applications
- Star connections are commonly used for systems with a neutral wire requirement, such as domestic and commercial power distribution.
- Neutral Point: One of the significant advantages of the star connection is the provision of a neutral point. This neutral point can be used for grounding purposes and provides a reference point for single-phase loads or systems that require a neutral connection.
- Flexibility: Star connections provide flexibility in terms of connecting single-phase and three-phase loads within the same system. Single-phase loads can be connected between any phase and the neutral point without affecting the balance of the system.
- Grounding: The presence of a neutral point facilitates effective grounding, which is essential for safety and fault protection in electrical systems. Grounding helps to mitigate the risk of electric shock and provides a path for fault currents to return safely to ground.
- Phase Voltage Equal to Line Voltage: In a star connection, the phase voltage is equal to the line voltage. This simplifies the design and operation of electrical equipment and reduces the complexity of voltage calculations in the system.
- Balanced Loads: Star connections inherently balance the phase currents, assuming the loads are balanced. This leads to a more stable and efficient operation of the electrical system, minimizing losses and reducing the risk of overheating in conductors and equipment.
- Ease of Maintenance: Star-connected systems are often easier to maintain and troubleshoot due to the presence of the neutral point and the balanced nature of the phase currents. Faults and issues can be localized more easily, leading to quicker diagnosis and resolution.
- Lower Voltage Stress: Compared to delta connections, star connections typically result in lower voltage stresses on electrical equipment and insulation materials. This can contribute to longer equipment lifespan and reduced risk of insulation breakdown.
- Wider Availability of Equipment: Many electrical devices and appliances are designed for use in star-connected systems, making it easier to source compatible equipment and components for installation and replacement.
- Delta connections are frequently used in industrial applications where a neutral connection is not needed, and higher line voltages are preferred.