Basic Principle of step down transformer
A transformer whether its Step down transformer or Step up transformer ,they work on the same basic principle which is called Electromagnetic Induction. A transformer is an electrical device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through mutual electromagnetic induction.
What is Electromagnetic Induction?
This phenomenon was first discovered by Michael Faraday in the 1830s and is a foundational concept in the field of electromagnetism.
Mutual Inductance: When two coils are placed close to each other, changing the current in one coil induces an EMF in the other coil. This is referred to as mutual inductance and is the basis for the operation of transformers.
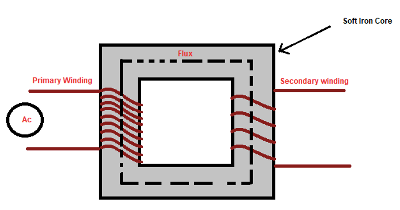
According to Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, when a coil is placed within a changing magnetic field, an electromotive force (EMF) or voltage is induced in the coil. The magnitude of the induced EMF is directly proportional to the rate of change of magnetic flux through the coil.
Mathematically, Faraday’s law is expressed as:
Es=−Ns *dΦ/dt
- Es is the induced EMF in the secondary coil.
- Ns is the number of turns (windings) in the secondary coil.
- dΦ/dt represents the rate of change of magnetic flux.
Magnetic Flux: Magnetic flux (Φ) is a measure of the magnetic field passing through a surface. It is calculated as the product of the magnetic field strength (B) and the surface area (A) perpendicular to the field:Φ=B⋅A
Mathematically, the voltage transformation ratio (k) is given by:
k=Es/Ep=Ns/Np
- Ep is the voltage applied to the primary coil,Np-No.of turns in Primary side
- Es is the voltage induced in the secondary coil,Ns-No.of turns in Secondary side
Thus a step down transformer is a type of electrical transformer that reduces the voltage from its primary winding to its secondary winding. In other words, it “steps down” the voltage level.It also means that for a step down transformer no.of primary winding will be more than secondary winding.
Applications:
-Power is usually generated at 11kv in generating stations and it is stepped up to higher voltage levels using Step-up transformers and it is then transmitted near load centers to minimize line losses.In Grid substations which are located near load centers ,we use step down transformers to supply it to consumers.
-Step-down transformers are commonly used in power distribution systems to reduce the high-voltage electricity generated at power plants to lower and safer voltages for use in homes and businesses.
-They are used in electronic devices to provide lower voltages for circuit components, making it safe for consumer use.
Isolation Transformers: In some applications, step-down transformers are used to provide electrical isolation between the input and output circuits, protecting sensitive equipment.
-In some lighting systems, step-down transformers are used to provide the appropriate voltage for certain types of lighting, such as halogen lamps.
The primary purpose of an isolation transformer is to isolate the powered device or equipment from the power source. Here are some key points about isolation transformers:
- Electrical Isolation: The primary and secondary windings of an isolation transformer are electrically separated, which means there is no direct electrical connection between the input and output sides. This isolation helps protect devices from voltage spikes, noise, and other electrical disturbances.
- Purpose:
- Safety: Isolation transformers are commonly used to enhance electrical safety. They help prevent the transfer of electrical noise, ground loops, and potential differences between the input and output.
- Equipment Protection: They protect sensitive equipment from power surges, voltage spikes, and other electrical issues that can damage or affect the performance of electronic devices.
- Ground Isolation: Isolation transformers can break the ground loop, which is a potential source of interference and noise in electrical systems. This is particularly important in audio and video systems where unwanted noise can degrade signal quality.
- Medical Applications: Isolation transformers are frequently used in medical equipment to ensure patient safety. They help prevent the flow of leakage current, protecting patients from electrical shocks.
- Construction: Isolation transformers are typically constructed with a special winding arrangement to provide electrical separation. The transformer may have a 1:1 turns ratio, meaning the input and output voltages are the same.
You may read about tap changers in a transformer here.
FAQs on step down transformers:
1. What is a Step-Down Transformer?
A step-down transformer is a type of transformer that reduces the voltage level from its primary winding to its secondary winding. It has fewer turns on the secondary side than the primary side, resulting in a lower output voltage compared to the input voltage.
2. How does a Step-Down Transformer work?
The transformer operates based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When an alternating current (AC) flows through the primary winding, it induces a magnetic field, which, in turn, induces a voltage in the secondary winding. The turns ratio determines the voltage transformation.
3. What are the typical applications of Step-Down Transformers?
Step-down transformers are commonly used to supply lower voltage levels to electrical devices. They are widely used in power distribution, appliances, electronic equipment, and various industrial applications.
4.What is the Turns Ratio of a Step-Down Transformer?
The turns ratio of a step-down transformer is the ratio of the number of turns in the primary winding to the number of turns in the secondary winding. It determines the relationship between the input and output voltages.
5. Can a Step-Down Transformer be used in reverse as a Step-Up Transformer?
While transformers are designed for specific voltage transformations, a step-down transformer can technically be used in reverse to increase voltage. However, it is not the most efficient or practical way to achieve voltage increase, and dedicated step-up transformers are generally preferred for such applications. - What are the advantages of using Step-Down Transformers?
Voltage Reduction: The primary purpose is to reduce the voltage from a higher level to a lower level suitable for various applications.
Isolation: Like other transformers, step-down transformers provide electrical isolation between the primary and secondary circuits. - How are Step-Down Transformers rated?
Step-down transformers are rated based on their power capacity, given in volt-amperes (VA) or kilovolt-amperes (kVA), and the turns ratio. Voltage and current ratings for both primary and secondary sides are specified.