Why do we conduct tan delta test of cables?
Tan delta test of cables is done to find out healthiness of cable insulation.Insulation is basically outer layer of the cables which is used to insulate the conductors inside. What is a tan-delta test & how it is done has been explained here.
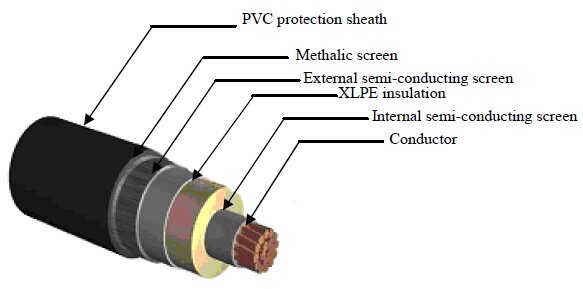
XLPE (Cross link polyethylene) cables are used for high voltage transmission of power and due to high voltage flowing in the conductors inside the cable, their outer layer is shielded in many layers to provide good insulation, this insulation of cable may also get poor due to moisture ingress, outer layer degradation, aging etc. It is therefore necessary to perform Tan delta test of cables periodically to avoid flashovers and breakdowns.
(PC-emworks.com)
Key features and characteristics of XLPE cables are following:
- Insulation Material:
- The primary insulation material in XLPE cables is cross-linked polyethylene. This process involves chemically bonding the polymer chains, improving the material’s resistance to heat and pressure.
- Thermal Stability:
- XLPE insulation provides excellent thermal stability, allowing the cable to operate at higher temperatures without losing its electrical properties. This makes XLPE cables suitable for both high and low-temperature environments.
- High Voltage Capability:
- XLPE cables are commonly used for high-voltage applications, including power transmission and distribution. They can handle high voltage levels while maintaining reliable insulation.
- Low Dielectric Loss:
- XLPE exhibits low dielectric loss, which means that a minimal amount of electrical energy is lost as heat during the transmission of power through the cable.
- Resistance to Chemicals:
- XLPE insulation is resistant to various chemicals, oils, and solvents, contributing to the durability and longevity of the cables.
- Moisture Resistance:
- XLPE cables have good resistance to moisture, reducing the risk of insulation breakdown due to water ingress. This property is particularly important for outdoor or underground installations.
- Flexibility:
- XLPE cables are generally more flexible compared to some other types of cables, allowing for easier installation and routing in confined spaces.
- Mechanical Strength:
- Cross-linking enhances the mechanical strength of the insulation, making XLPE cables more robust and able to withstand mechanical stresses during installation and operation.
- Lightweight:
- XLPE cables are relatively lightweight compared to some alternative cable types, making them easier to handle and transport.
- Low Smoke Emission:
- In the event of a fire, XLPE insulation tends to produce low levels of smoke and toxic gases, contributing to improved safety in indoor environments.
- Environmental Friendliness:
- XLPE cables are considered environmentally friendly because they do not contain hazardous materials such as lead or cadmium. However, proper disposal practices should be followed.
- Wide Range of Applications:
- XLPE cables are used in various applications, including power distribution networks, underground and submarine installations, industrial facilities, renewable energy projects, and high-voltage transmission lines.
- Jacketing Options:
- XLPE cables may have an additional outer layer or jacket for mechanical protection, UV resistance, and added insulation in certain applications.
Basic Principle of tan delta test of cables
Basic principle of tan delta test of cables or equipment like CT,CVT etc is same, If the insulation of a cable is free from defects, like water trees, electrical trees, moisture and air pockets, etc, the cable insulation will behave like a perfect capacitor. If there is some impurity or defect in the insulation, there will also be resistive component other than the capacitive one and thus there will be resistive current component and a high tan delta value.
An ideal cable will be very similar to a parallel plate capacitor with the conductor and the neutral being the two plates separated by the insulation material.
Watch this video by Megger, step wise method has been explained in a clear manner:
Interpretation of Tan delta test of cables
- A low Tan delta test of cables value indicates good insulation, as it means there is minimal dielectric loss.
- A high Tan delta test of cables value suggests that the insulation may be deteriorating, possibly due to moisture ingress, aging, or other factors.
- A significant increase in tan δ compared to previous test results can be a warning sign of insulation problems.
Water trees: They are tree shaped channels found within insulation of cable due to moisture ingress. These trees in presence of electrical field cause partial discharge which can lead to insulation failure. An over voltage can also cause water tree.
What is Partial discharge?
Partial discharge (PD) is a localized electrical discharge that occurs within the insulation or dielectric materials of electrical equipment or systems. It is a phenomenon where a small amount of electrical energy is discharged in a localized area, but it doesn’t lead to a complete breakdown of the insulation.
Partial discharge cable testing technology has advanced to the level where we can accurately determine location of fault and severity of cable flaws.PD is often measured in picocoulombs (pC) or other similar units, representing the charge associated with each discharge event. Monitoring PD is crucial to identifying potential insulation problems before they escalate.

Testing steps
- Cable to be tested must be isolated from system and de-energized.
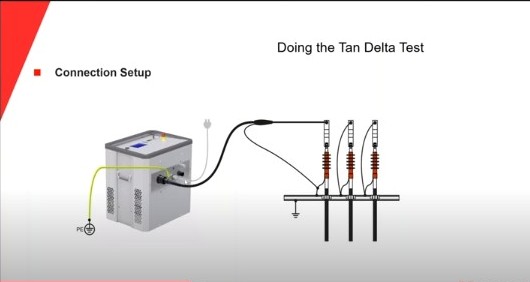
- A tan-delta test kit is used for testing, it has a voltage source which is required to energize the cable. We use Very Low Frequency (VLF) A.C Hipot (High potential).VLF hipots are also widely used for testing newly installed or repaired cable before re-energizing to insure the cable is sound and for testing critical cable runs.
- Test voltage is raised and tan-delta values are recorded. If a cable’s insulation is perfect, tan delta will change little as the applied voltage is increased. The capacitance and loss will be similar with 1 kV or 10kV applied to the cable. It is to be noted that tan-delta values and voltage levels are dependent in old cables it means when higher voltage is injected its tan delta values may also increase.
(PC-Megger.com)
- For shielded cable testing, the HV lead of the kit is connected to the cable conductor and the cable shield or sheath is effectively grounded. The test is conducted in the GST mode as measurement is taken wrt ground.
- For unshielded cables : Reading is taken in UST mode and any other cables not included in the test should be effectively grounded.
- Tan delta tests can’t detect the location of fault in a cable ,the cable from point A to point B being tested only gives an assessment of the insulation quality between those points.
FAQs:
When should tan delta testing be performed on cables?
- This should be conducted during routine maintenance or as part of a preventive maintenance program. The frequency of testing can vary based on factors such as cable age, environmental conditions, and criticality.
Can the testing be performed on live cables, or does the cable need to be de-energized?
- Tan delta testing is typically performed on de-energized cables to ensure the safety of personnel. However, there are advanced diagnostic methods that can be conducted on live cables using special techniques and equipment.
What do I do if test results indicate a problem with a cable’s insulation?
- If the test results reveal a high tan delta value or significant deviations from previous tests, it’s essential to investigate and address the issue. This may involve further diagnostic testing, maintenance, or even cable replacement.
- For more information see this.