What is a Potential transformer and capacitive voltage transformer, Is there a difference between the two?

Potential transformer– Potential transformer is used for measurement as well as protection purpose of equipment in a substation. It’s purpose is to step down High Voltage to low voltage so that it can be easily read by measuring instruments, a potential transformer operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction. It uses a primary winding connected in parallel with the high voltage circuit and a secondary winding connected to the measuring or protection instruments. A P.T is generally used in Bus-coupler bay in a substation & it measures bus voltage in the substation.
Capacitive Voltage Transformer: A capacitive voltage transformer operates on the principle of capacitive voltage division. It consists of a series capacitor connected in the high voltage circuit and a capacitive voltage divider .It is generally used in line bays i.e for feeding/receiving power to/from transmission lines. CVT with wave-trap is used in Power line carrier communication ,for filtering of communication signal from power signal & Substations also communicate with each other through this channel, they are also used for protection of lines. If one end of transmission line has tripped, other end gets also tripped by PLCC protection scheme.
In power systems, communication signals are often transmitted through power lines using power line carrier communication. Line traps prevent these communication signals from interfering with other parts of the power grid.
What is standard output voltage of potential transformer/CVT?
Usually it is 110v , it means that when the primary line voltage is suppose 132kv then secondary line voltage will be 110v (line voltage is voltage between any two phase in a three phase system).If the primary voltage is P (Kv), then its ratio is P (kv)/110v.
Thus PT ratio is P (KV) /110 V.
Nowadays use of wave-trap has been limited due to introduction of OPGW -Optical fibre ground wire being used in transmission lines in place of earth wire, OPGW serves dual purpose of shielding of conductors from lightning strikes like conventional earth wires and it also has optical fibres which can be used for communication, data transfer and Protection.
Optical Fiber Ground Wire (OPGW) is a type of cable that combines optical fibers for communication and metallic wires for electrical grounding purposes. It is commonly used in the electrical utility industry, particularly in high-voltage overhead transmission lines.
Both P.T and C.V.T look alike from outside.
Testing and commissioning of P.T and C.V.T
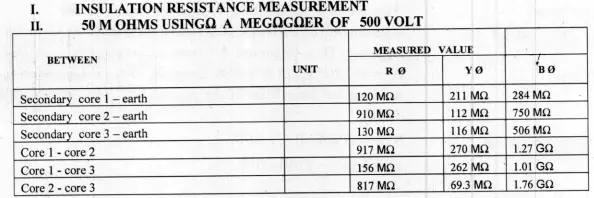
By conducting below mentioned three important tests, we can successfully commission CVT/P.T. As explained in case of C.T ,PT and CVT also have many cores which are used for different purpose. Pre-commissioning Testing is done on different cores. Voltage ratio test, Insulation resistance test, Secondary winding resistance tests are conducted .
- IR tests are conducted as follows:
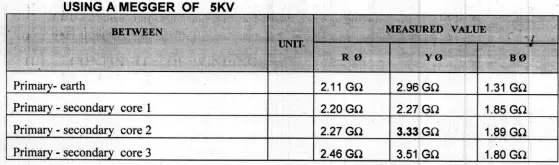
(Readings mentioned below is a sample reading)
2.Secondary winding resistance readings are taken as follows:

By factory it implies test results of CVT/PT conducted in manufacturers factory & Site implies where the equipment is to be installed.
3.Voltage ratio test readings are taken as follows:
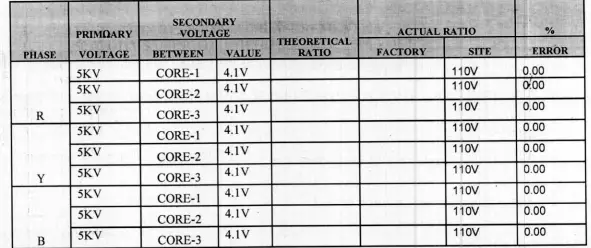
After getting all above satisfactory readings, we can successfully commission the P.T/C.V.T.
You may watch this for more:
FAQs:
- What is a Capacitive Voltage Transformer (CVT)?
A CVT is an instrument transformer used to measure high voltage levels in power systems. It transforms high voltage into a lower, safer voltage for measurement and protection purposes. - How does a CVT work?
CVTs work based on the principle of capacitance. They consist of a capacitive divider and a secondary winding that provides the reduced voltage output, which is proportional to the high voltage input. - What are the primary applications of CVTs?
CVTs are primarily used in voltage measurement, protection, and control systems in high-voltage substations. They help in monitoring and safeguarding the power grid. - What are the advantages of using CVTs?
- High Accuracy: CVTs offer accurate voltage measurement.
- Isolation: They provide electrical isolation between the high-voltage system and measurement devices.
- Compact Size: CVTs are relatively compact compared to other voltage measurement devices.
- Can CVTs be used for both indoor and outdoor applications?
Yes, CVTs are available in both indoor and outdoor configurations, depending on the specific requirements of the substation. - What is a Potential Transformer (PT)?
A PT, also known as a voltage transformer, is an instrument transformer used to measure voltage levels in power systems. It reduces high voltage to a safe and standardized level for measurement and protection. - How does a PT work?
PTs use the principle of electromagnetic induction. They have a primary winding connected to the high-voltage side and a secondary winding that provides a lower-voltage output proportional to the input voltage. - What are the primary applications of PTs?
PTs are used for voltage measurement, protection, and control in power systems, similar to CVTs. They play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and reliability of the grid. - What are the advantages of using PTs?
- High Accuracy: PTs provide accurate voltage measurement.
- Electrical Isolation: They offer electrical isolation for sensitive measuring and protection devices.
- Durability: PTs are designed to withstand the rigors of high-voltage environments.
- Are there any limitations to using PTs?
- Cost: PTs can be relatively expensive, especially for high accuracy applications.
- Size and Weight: They are bulkier and heavier than CVTs.
- Can PTs be used for both indoor and outdoor applications?
Yes, PTs are available in indoor and outdoor configurations, and the choice depends on the specific needs of the substation and environmental conditions. - Are CVTs and PTs interchangeable?
While both CVTs and PTs are used for voltage measurement, they are not interchangeable due to differences in their operating principles and characteristics. The choice between them depends on the specific application and requirements. - What are the maintenance requirements for CVTs and PTs?
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the accuracy and reliability of CVTs and PTs. This includes testing, calibration, and visual inspections as per manufacturer recommendations and industry standards. - Are there standards and regulations governing the use of CVTs and PTs?
Yes, there are international standards and regulations, such as IEEE and IEC standards, that provide guidelines for the design, testing, and application of CVTs and PTs to ensure their reliability and safety in power systems. Compliance with these standards is essential.
Visit this link for more information.