Transformers work on principle of electromagnetic induction , their primary purpose is to change (Increase or decrease) voltage level. Types of transformers depend on their construction, application, and voltage levels.
Main types of transformers:
1.Types of transformers on the basis of Input/Output Voltage level :
- Step-Up Transformers: Output voltage is more than Input voltage , it means that these transformers increase the voltage level from primary winding to secondary winding. They are commonly used in power generating stations to step up the voltage for long-distance power transmission, to reduce energy loss.
- Step-Down Transformers: Output voltage is less than Input voltage , it means that step-down transformers decrease the voltage level from primary to secondary winding. They are used in various applications where lower voltage is required, such as in households to reduce the voltage from the power grid.
2.Types of transformers on the basis of Power rating:
- Distribution Transformers: These transformers are used in the distribution network to step down the high voltage from transmission lines to lower voltages suitable for commercial and residential use. They are usually pole-mounted or pad-mounted.
- Power Transformers: Power transformers are large transformers ,their capacity range from 05 Mva to higher and primarily used in power generation and transmission systems to step up or step down voltages as needed for efficient transmission and distribution of electrical energy.
3.Transformer as measuring device :
Instrument Transformers: Instrument transformers include current transformers (CTs) and potential transformers (PTs).Both CTs and PTs reduce the incoming current and voltage respectively to a proportionate lower value to easily measure them. CTs are used to measure high currents by producing a reduced current proportional to the current flowing through the conductor, while PTs are used to step down high voltages for measurement and protection purposes.
4.Transformer as Isolating/protective device :
Isolation Transformers: Input and output voltage remains same in this transformer, these transformers are used to electrically isolate two circuits Input and Output while allowing the transfer of power between them. They provide safety by preventing direct electrical contact between the input and output circuits.
5.Types of transformers depending on no. of windings:
- Single winding transformer or Auto Transformers: Auto transformers have a single winding with a portion of it common to both the primary and secondary circuits. They are used for voltage regulation, impedance matching, and to provide a different voltage level from the input to the output simply by moving tap positions. They are also used at higher voltage levels as they are more economical than two winding transformer.
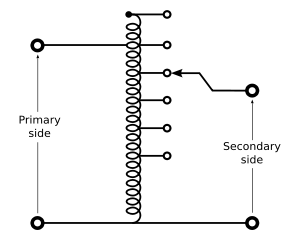
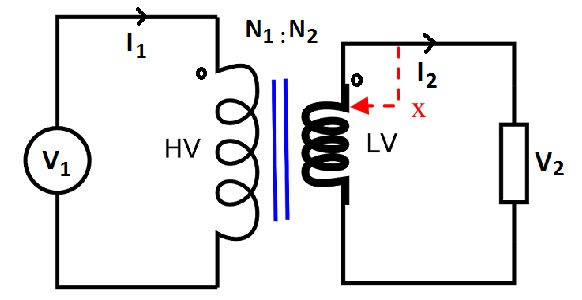
2. Two winding transformer : These transformers have two windings Primary and Secondary and they are most common type of transformer. Below drawing is of step down transformer and primary winding is high voltage (HV) side and secondary winding is low voltage (LV) side.
3. There are also three winding transformers , the third winding is called tertiary winding ,it is used where two different output voltages may be required.
6.Types of transformers on the basis of construction
Depending on the placement of the magnetic core, Transformers can be categorized into the shell type and core type. For core-type transformers, the windings encircle the core, while in shell-type transformers, the core encircles the windings.
A transformer core is a structure of thin laminated sheets of ferrous metal (most commonly silicon steel) stacked together, on which the primary and secondary windings of the transformer are wrapped around.
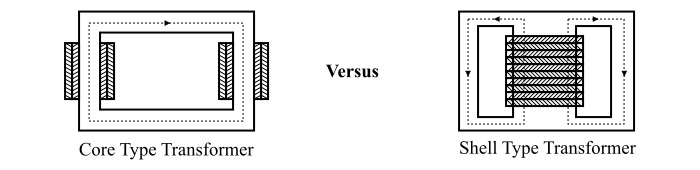
(i) Core type transformer
In core type design , the windings of the transformer surround the core steel. In this type, there is no return path (or closed loop) for the magnetic flux around the coils. The half of each winding (primary and secondary windings) is placed on each limb (vertical part) of the core, so that the leakage flux can be minimized. This type has easy assembly of windings and insulation, and has simple structure, electrical transformers often use core type structures. This design typically yields more energy losses, and it requires more copper or aluminum winding material than a shell-type configuration.
(ii) Shell type transformer
In a shell type transformer, both primary and secondary windings are placed on the central limb. The shell type cores are used for lower power applications. Though they have less energy losses, but their maintenance is harder because the windings are harder to reach.
Thus the most significant difference between shell and core types is that the core type transformers are suitable for high-voltage and high-power applications, whereas the shell type transformers are most suitable for low-voltage and low-power applications.
Related articles:
220/132 KV Grid Substation Overview
Understanding Transformer Testing-09 Important electrical tests
Why is DGA analysis of transformer oil important? 12 Important Properties.