
Transient Response Analysis- The study of behavior (Output/Response) of a system with respect to time is called Time Response analysis. Time response is divided into two parts:
Transient Response Analysis
It is the response /Output before reaching the steady state or final value. The transient state is the short-term, temporary response of a system after a sudden change in input or conditions. During this period, the system is not yet stable and may exhibit oscillations, overshoots, or undershoots. Transient behavior typically diminishes over time as the system reaches equilibrium.
Steady State Response Analysis
The time response or part of the response after vanishing the transient part.
Thus Transient response analysis is the study of a system’s behavior during the period after a change in its input but before it reaches a steady state. This analysis focuses on how the system responds to changes, such as switching on or off, sudden changes in input signals, or faults, before the system settles into its final, steady condition.
Energy storage elements in the electrical system are- Inductor and Capacitor.
• Initial conditions are evaluated at the time instants t=0-, t=0+ and t>0 i.e before, just and after switching action respectively.
The voltage and current relationship for inductor and capacitor are given below:
- Inductor:
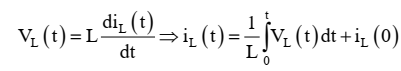
From above equation we can write i(t) as :
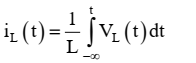
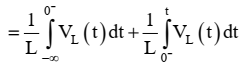
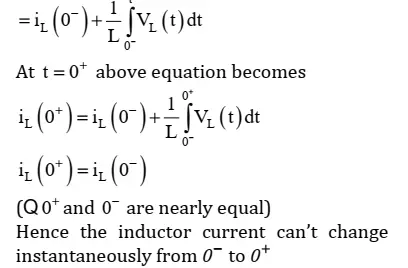
2. Capacitor:
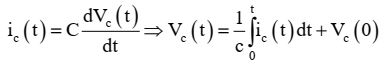
At t 0 = + above equation can be written as
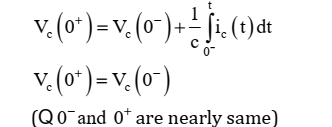
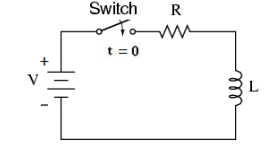
In the above circuit S is a switch and the arrow indicates that at time t=0 the switch is closed. When the switch is closed, suddenly a huge amount energy flows from source to the circuit. This state of the circuit just after the switch is closed is called transient state. The resulting voltages and currents change w.r.t. time and they are called transient response analysis.
A circuit having constant sources (i.e. dc sources or sources with same frequency, ω) connected for long time is said to be in steady state. Current and voltage do not change with time in steady state. Ideally after infinite amount of time and practically after 5 time constants circuit enter into steady state.
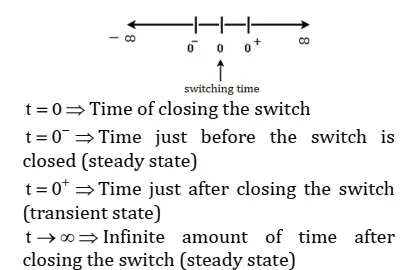
The behavior of inductor and Capacitor at t=0+ and t → ∞ is following :
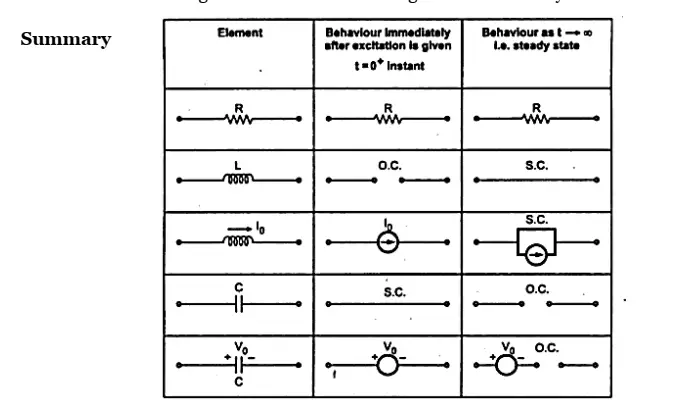
To find the steady state values :
i) Current through the inductor is maximum at steady state and would be calculated by replacing the inductor by short circuit. i.e., iSC=iL(0-) = iL(0+)
ii) Voltage across the capacitor is maximum at steady state and would be calculated by replacing the capacitor by open circuit. i.e., Voc= Vc(0-)=Vc(0+).
the circuit at t=0- .The switch will remain closed at t=0 circuit is in steady state hence inductor will be short circuited.
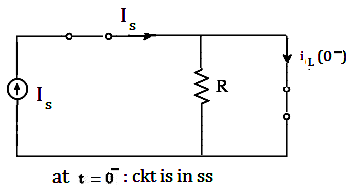
i L(0-) = Is=i L(0+)