Auto-reclosing
As the name suggests Auto re-closing is a scheme/mechanism where a particular breaker pole (phase) Automatically re-closes after tripping on transient (temporary) fault in a transmission line. Normally in 132kv or below voltage transmission lines ,when a fault occurs in the line ,all its poles (phases) are tripped which results in power interruption, however we require a system for higher voltage levels as they transport bulk power ,where only that phase should trip which senses the fault and power should flow from remaining phases without interruption. Auto-reclosing scheme is used to address this issue in a Transmission line of 220kv and higher voltage levels.
Why do we need Auto Re-closing Scheme ?
High voltage transmission lines evacuate a huge amount of electric power from generating stations and power grids. It is therefore desirable that there is minimum power interruption in the system and continuation of power flow through the lines should not be interrupted for a long time. A 500 MW generating station may trip if its power evacuating transmission lines trip due to some fault in the line. Auto Re-closing scheme is for transient faults which occur for very short duration of time.
Due to bad weather a tree branch may touch the conductor temporarily, or a tree branch may touch the line and break due to burning, these situations are transient in nature and HV overhead lines in forest areas are prone to this type of fault ,therefore in this scheme that particular phase gets tripped which detects the fault and after this it waits for few seconds for fault to get cleared and then again closing command is sent to that particular phase of breaker.
Most faults in overhead transmission lines are single-line-to-ground (SLG), and 80–90% of the faults are transient . Temporary faults are intermittent and stay for a short duration; therefore, they can be easily eliminated by isolating the faulted phase from healthy phases.
Reclosers are protective devices used to remove temporary faulty phases and deionize arc faults without interrupting the energy flow. Auto-reclosers must differentiate the nature of fault before reclosing as reclosing is not desired when the nature of fault is permanent and desired when it is transient. The auto-reclosing system attempts to close the circuit breaker multiple times until the fault clears. If the fault persists, the system permanently opens the circuit breaker.
A set time delay can help clear semi-permanent faults before reclosing. Permanent faults, such as broken conductors, and faults on underground cable sections, must be located and repaired before the supply can be restored. Sufficient time must be allowed after tripping for the fault arc to de-energise prior to reclosing otherwise the arc will re-strike.
TYPES OF AUTO-RECLOSING SCHEMES
Auto-reclosing is a protection scheme for power systems. It identifies the nature of fault as either temporary or permanent and isolates the temporary faults from the remaining electrical transmission system and recloses them subsequently. For permanent faults, the auto-recloser is blocked, and the faults must be manually rectified.
Auto-reclosing is divided into three main types :
(i) Single-phase auto-reclosing (SPAR),
(ii) Three-phase auto-reclosing (TPAR), and
(iii) Multi-phase auto-reclosing (MPAR).
In SPAR schemes, after fault nature identification and secondary arc verification, only the faulty phase is disconnected
and reclosed
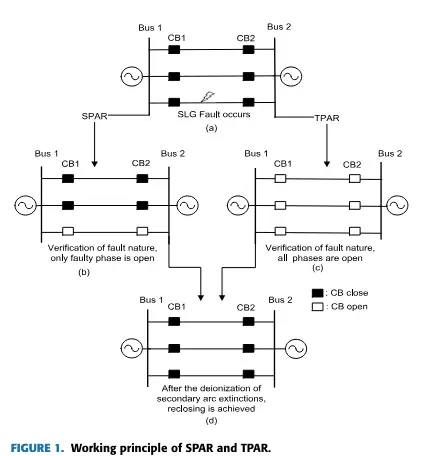
When the SLG fault intercepts the phase of the transmission line in Fig. 1(a), the Auto re-closing scheme verifies the nature of the fault as ither temporary or permanent. For SPAR, in case of a temporary fault, secondary arc detection, and finding arc extinction, the faulty phase is disconnected from the transmission system, as shown in Fig. 1(b). Similarly, for TPAR, all phases are disconnected from the
transmission line, irrespective of SLG or multi-phase faults, as shown in Fig. 1(c). Likewise, after secondary arc extinction verification, the faulty phase is reclosed for SPAR and all phases are reclosed for TPAR, as shown in Fig.
In SPAR, the remaining healthy phases continue to power without any delay during faulty phase disconnection. Unfortunately, power continuity is disrupted in the TPAR scheme.
COMMUNICATION-BASED SCHEMES
In these schemes, electrical parameters from both terminal sides of power system transmission are required through a communication channel (PLCC).
By analyzing the differences in PLCC signals before and after the fault, secondary arc extinction is determined, and the Auto re-closing command is given to the circuit breakers. Owing to the advancements in modern communication technology, these Auto re-closing schemes are commonly used for power system protection to accurately predict the abnormal behavior of signals during a fault. Such schemes have been the cause of a substantial improvement in continuity of supply.