Introduction:
DGA analysis (Dissolved gas analysis) of transformer oil is one of the tests that is conducted on transformer oil to know about various gases present in the oil of a transformer which in turn gives us information to assess health of a transformer. Testing of transformer oil is analogous to testing of human blood ,as human blood tests reveal a lot of information about overall health of a human ,in a similar way Testing of transformer Oil also reveals a lot of information about its inner health.
Transformer oil, also known as insulating oil, possesses high dielectric strength and thermal conductivity, allowing it to withstand high voltages and dissipate heat effectively. It serves dual purpose of cooling the transformer and acting as insulation.
Transformer oil goes through various stress and contamination during its operation, therefore it is necessary for periodic checking of transformer oil to assess its health .
Properties of transformer Oil
The properties of transformer oil are crucial for the efficient and safe operation of transformers. Here are some key properties of transformer oil:
- Dielectric Strength (BDV Test):
- Transformer oil must have a high dielectric strength to withstand the electric field within the transformer. This property helps prevent electrical breakdown or arcing.
- Transformer oil must have a high dielectric strength to withstand the electric field within the transformer. This property helps prevent electrical breakdown or arcing.
- Viscosity:
- Viscosity is the measure of the oil’s resistance to flow. The oil should have appropriate viscosity to ensure effective cooling and heat dissipation within the transformer.
- Flash Point:
- The flash point is the temperature at which the oil vaporizes to form a flammable mixture with air. A high flash point is essential to minimize the risk of fire in case of a fault.
- Pour Point:
- The pour point is the lowest temperature at which the oil retains its fluidity. A low pour point is necessary to maintain the oil’s flow characteristics, especially in cold environments.
- Moisture Content:
- Transformer oil should have low moisture content to prevent the formation of sludge and reduce the risk of electrical breakdown. Moisture can also contribute to the formation of acids, affecting the oil’s stability.
- Acid Number:
- The acid number measures the acidity of the oil, indicating the extent of oxidation and the presence of acidic by-products. A low acid number is desirable for the longevity of transformer insulation.
- Oxidation Stability:
- Transformer oil needs to resist oxidation, which can lead to the formation of sludge and acids. Oxidation stability ensures that the oil maintains its performance over an extended period.
- Color:
- The color of transformer oil is an indicator of its purity. Clear and bright oil is preferred, and any discoloration may suggest contamination or degradation.
- Interfacial Tension:
- Interfacial tension measures the oil’s ability to separate from water. High interfacial tension is essential to prevent the emulsification of water in the oil.
- Specific Gravity:
- Specific gravity is the ratio of the density of the oil to the density of water. It provides an indication of the oil’s purity and can help detect contaminants.
- Gas Content:
- The presence of gases, such as oxygen and nitrogen, can affect the insulating properties of the oil. Transformer oil is sometimes degassed to remove these gases.
- PCB Content (Polychlorinated Biphenyls):
- Transformer oils should be free from PCBs, as these chemicals are toxic and have been banned due to environmental concerns. Oils with PCB content are considered hazardous.
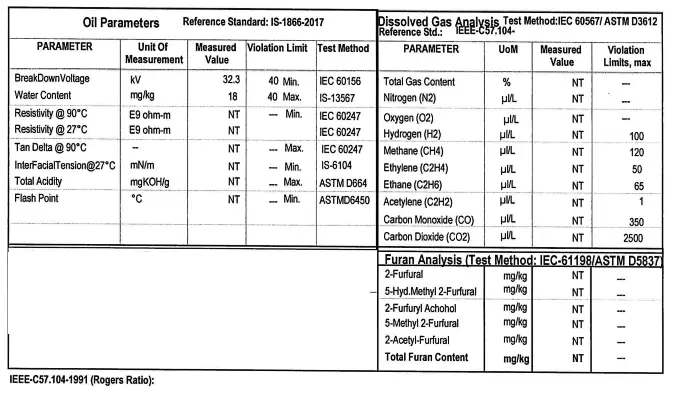
Below table mentions all standard tests including DGA analysis (Dissolved Gas Analysis) which are conducted on transformer oil and violation limit is also indicated against each test. We will understand each of them one by one.
Types of testing of transformer oil and DGA analysis :
1.Breakdown voltage test (Dielectric strength test): It is maximum voltage required to produce a dielectric breakdown through the material (Oil in this case) and it is measured in Kilo-volts (KV) per standard thickness of the insulating medium. High value of breakdown voltage (BDV) indicates that oil is free from moisture and conducting materials and a low value of BDV indicates presence of moisture content and conducting substances in the oil.
2.Water content (PPM) : It measures amount of moisture in the transformer oil, moistures in oil can lead to insulation breakdown and reduced dielectric strength. Water content in the oil also impacts the insulating materials aging rate. Transformers may even go into breakdown if excessive water content is found in the insulation.
3.Resistivity(Specific resistance) :The specific resistance of oil measures DC resistance between two opposite sides of one m3 block of oil. Its unit is ohm-m at a specific temperature. With increase in temperature the resistivity of oil decreases rapidly. Minimum standard specific resistance of transformer oil at 90oC is 35 × 1012 ohm–cm and at 27oC it is 1500 × 1012 ohm–cm.
4.Tan-delta (Dielectric dissipation factor) : A Tan Delta test is performed by applying an Ac voltage to a test cell of known gap, total current flow through the oil is measured and reactive and resistive part of current is separated. If the oil is free from contamination, the oil and the electrodes that it separates (e.g. transformer HV windings and the grounded tank) closely exhibits the properties of a perfect, parallel plate capacitor.
If there is some contamination in the oil, the resistance of the insulation decreases, resulting in measurable and increasing resistive current through the insulation/capacitor. Tangent of the delta which is angle between IC & IR, is given by IR / IC, when this angle is zero, the Tan Delta is 0%, indicating that the oil has no losses.
As losses in the oil increase, the resistive current contribution also increases, and δ subsequently increases which in turn increases tan delta. Thus higher the value of tanδ more is contamination in the oil. Tan delta test is also performed on bushings and windings of a transformer using a tan-delta test kit.
5.Interfacial tension: It measures the ability of the transformer oil to resist emulsification. It indicates the oil’s ability to separate from water or solid contaminants, ensuring the insulation properties remain intact.
6.Total Acidity: If transformer oil becomes acidic, the water content in the oil will become more soluble in the oil. The acidity of oil will deteriorate the insulation property of paper insulation of windings. Acidity accelerates the oxidation process in the oil. Acid also includes rusting of iron in the presence of moisture.
7.Flash point: Flash point of transformers oil is that value of temperature at which oil starts vaporizing.
DGA Analysis (Dissolve Gas Analysis) test
When there is some fault or other issue in the inside of transformer, certain gases are produced due to the decomposition of the transformer oil. When the fault is major, the production of decomposed gases are significant and they also get collected in the Buchholz relay .In DGA Analysis of transformer oil ,gases in oil are extracted and analyzed to determine the quantity of gasses in a specific amount of oil.
By observing the percentages of different gases present in the oil, we can predict the internal condition of the transformer. If any of the gases are found in more than violation limit it indicates that some internal fault has occurred or hotspot has been formed or paper insulation deterioration has occurred. It is quite possible that even if the transformer oil passes the breakdown voltage (BDV) test, it may violate DGA analysis test limitations.
Following are different indications of violation limit of different gases in the DGA Analysis:
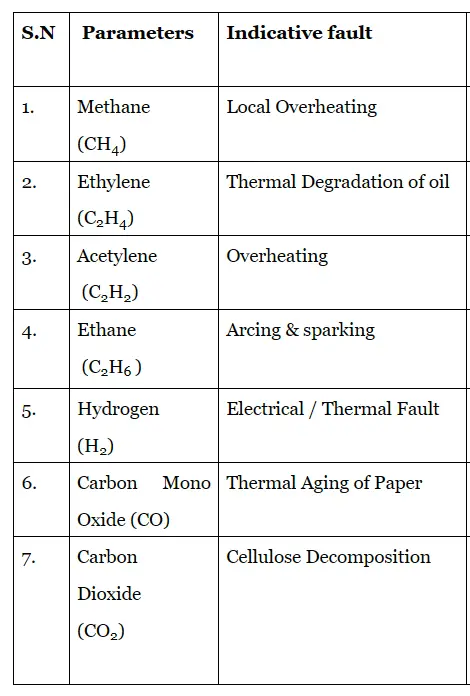
As above table clearly shows that different violation in DGA analysis indicate different underlying issues ,therefore this test is very important for assessment of internal health of a transformer.
Furan Analysis:
It measures the concentration of furanic compounds in transformer oil. Paper insulation of windings and cores are very important as they insulate from main body and other parts. It is therefore necessary to monitor the condition of paper insulation inside a power transformer. When breakdown of cellulose insulation paper of core and windings occurs compounds are formed which provides insights into the condition of the solid insulation system. In a transformer, the aging effect of paper insulation gets accelerated due to the oxidation that occurs in oil and it damages the insulation.
Sampling of transformer oil for testing purpose is equally an important skill and should be done carefully . You can read more about it here.