What is a differential protection relay?
There are two types of protection relays mainly used in a power transformer, one is main protection relay which is differential protection relay and another is backup relay which is also called over-current earth fault relay. Differential protection relay is mainly used for internal faults of transformer and backup relays are used for external faults.

(PC-tecquipment.com)
Working Principle of Differential protection relay
Differential protection relay is based on the principle that all current entering the Transformer or any equipment should be equal to the outgoing current (KCL). If there persists any fault inside a transformer, then the current entering the Transformer will not be same as current coming out of the transformer. Current transformers are installed on both the input and output sides of the transformer. The CTs accurately measure the current flowing into and out of the equipment. As differential protection relay in a transformer is used to detect internal faults ,we monitor fault current using bushing current transformer which are also called turret C.Ts.
Bushing C.Ts are located at bottom part of bushings , they can also be sometimes mounted on top cover area of the transformer. Bushing C.Ts only monitor the current which enters and exits the transformer. If we use field C.T (external C.T) then external faults shall also be picked up in differential relay which is not desired.
You may watch this for more clarity:
Types of faults which can be detected using a differential protection relay
1. Restricted Earth fault (REF) in the winding of the transformer. A winding may break and touch the body of transformer which is grounded and cause earth fault. It is called Restricted Earth fault because the differential protection only detects the fault within the Transformer, and it is within a restricted area. Unlike conventional earth fault protection that operates for any ground fault in the system, a REF scheme is designed to provide selective protection for internal faults in a transformer.
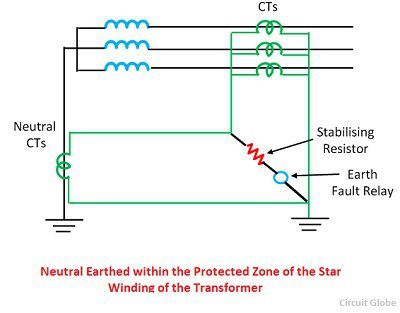
(PC-circuitglobe)
2.Fault due to gas formation inside the Transformer: Gas formation inside a transformer is typically associated with certain types of faults, issues, or abnormalities in the operation of the transformer. These gases are a result of chemical reactions and thermal stresses within the insulating materials and the oil used in the transformer. These faults are detected by Buccholz relay /Oil surge relay (OSR) which are gas actuated relays .
OSR and Buccholz relays are principally same, the former is used for main tank of transformer and the later is used in OLTC(On-load tap changer).These relays are also coupled with differential protection relay and their alarm and tripping is usually recorded in this relay ,separate auxiliary relays are provided for different faults which sends signal to differential protection relay.
Buchholz relay principle
The core principle of the Buchholz relay is to detect the accumulation of gas within the transformer’s oil. The Buchholz relay is equipped with a float-operated mechanism located in the oil-filled chamber of the transformer. This mechanism is sensitive to the flow of oil and gas. As gas is generated within the oil due to a fault, it rises to the top of the transformer tank, displacing oil. When a small amount of gas is generated, the float rises slightly due to the displacement of oil. This triggers the Buchholz relay to initiate an alarm signal.
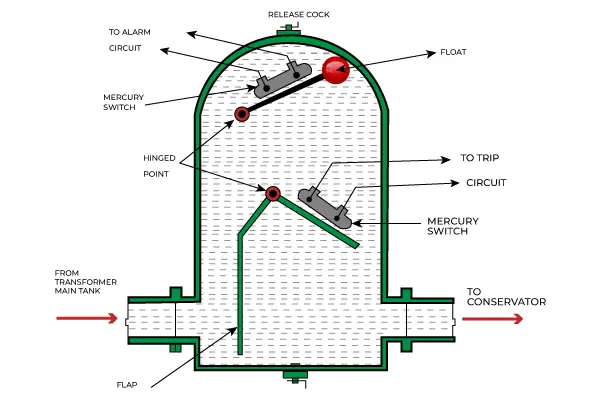
If the gas generation rate increases significantly, the float rises further, reaching a critical point. At this stage, the Buchholz relay initiates a trip signal, which can be used to disconnect the transformer from the power system by tripping the circuit breaker. This is a safety mechanism to prevent further damage and to isolate the transformer from the network.Buchholz relay also monitors the flow of oil.
A sudden loss of oil flow or a rapid drop in oil level can trigger the relay to issue an alarm or trip signal. This helps protect the transformer from mechanical and thermal stresses caused by a lack of oil circulation.
3. Fault due to excessive temperature of oil and excessive winding temperature of the transformer :It can also be indicated by differential relay. Excessive temperatures are detected by oil temperature indicator(OTI) and winding temperature indicator (WTI), probes attached to OTI and WTI are connected with the Transformer which continuously indicates the oil temperature and the winding temperature .OTI and WTI have mercury switches which make/break contacts to give alarm and tripping command. Alarm and trip temperatures are manually set in these indicators.

Stick like part is probe of the indicator, in case of OTI it is immersed in transformer oil in the main body and in WTI it is fitted with a heating resistance which is fed by a current proportionate to the current flowing through the transformer winding. This proportionate current is measured by bushing C.T , usually one of the phases of bushing C.T is used for WTI. In the name plate of the bushing C.T , it is mentioned that which phase and core is being used for WTI .
4. Abnormal pressure : Abnormal pressure inside the Transformer is built when an internal fault occurs which raises the oil temperature and results in formation of gases, this abnormal pressure is released by pressure relief device, this device is also connected with auxiliary relay and its alarm and trip indication is given in differential protection . When the pressure increases inside the transformer ,the top part opens just like pressure cooker valve. As soon as valve opens ,its N.O contact closes which sends +Ve supply to auxiliary relay and differential relay which sends tripping command to the circuit breaker .

5.Magnetic Oil Level gauge alarm: Magnetic Oil Level gauge(MOG) is round dial shaped oil level indicator which indicates level of oil in main conservator tank ,when oil leakage occurs in the transformer due to some fault or any other reason ,the oil flows from main conservator tank to transformer’s main body and due to this the mercury switch in MOG operates which gives command to alarm bell . MOG gives indication to differential relay which actuates auxiliary relay and alarm blows in the panel of the control room.
Below drawing is of Differential relay circuit and here it is mentioned as 87T relay. Please see that 30 A,B,C,D,E,F relays are auxiliary relays and their output contacts have been used to initiate alarm/trip indication in differential relay.
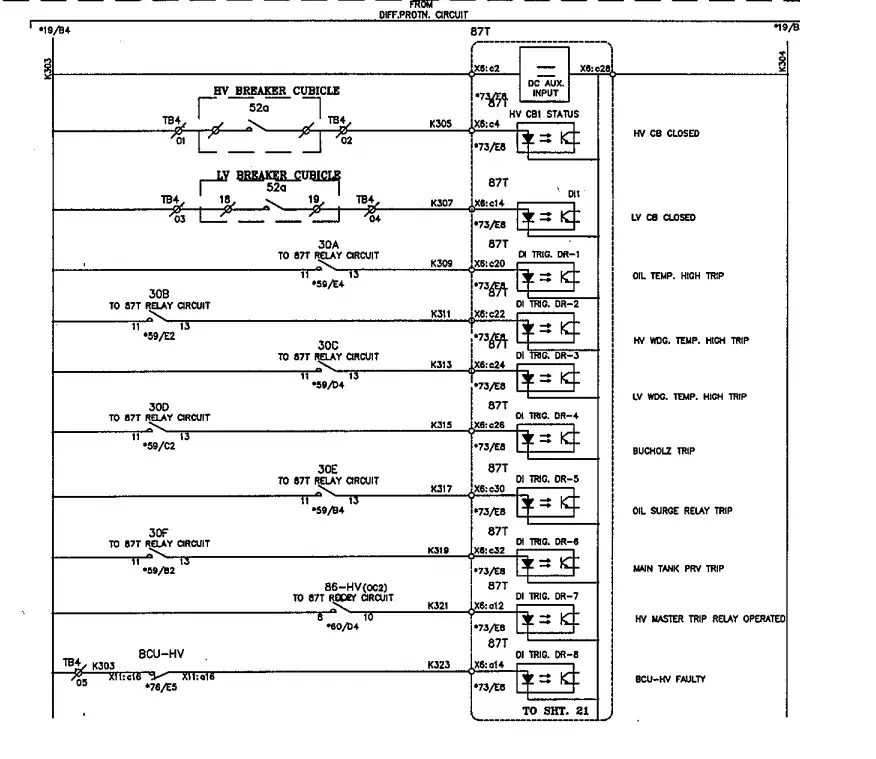
All above protection schemes of transformer can be implemented using a Differential relay. It is also to be noted that other than R.E.F protection other internal protection of transformer like OTI,WTI,OSR etc may or may not be configured through differential relay , they can be actuated using separate auxiliary relays to send alarm and trip commands.