
What if there is no D.c battery bank?
One may ponder why do we use DC bank in a substation where we have to deal with A.C supply ,where all switching operation is done on A.C supply only?
In order to understand this, let us suppose that everything worked on A.C supply in a substation ,what kind of problem we will face if we do not use D.C system:
- Unable to trip the circuit breaker in case of Power failure: Substations receive power from either adjacent substations or from generating station, in case of power failure from the generating station or the connecting substation ,none of the circuit breakers can be operated as the tripping and closing coil will need AC supply to operate. If some fault has occurred then isolating the faulty part either in substation or connected transmission line will be very difficult.
- Unreliable fault detection : A Fault has occurred and the fault sensing relays which are powered by A.C supply senses the fault and send tripping command to the circuit breaker tripping oil which is again operated by AC supply . As these operation need to happen very quickly and relay coils need to pickup instantly to send command to circuit breakers and the relays also need to be always energized, as AC supply voltage is not very stable & always available during disturbances ,therefore in order to deal with all above mentioned issues we need a stable, always available power source.
- Unable to get status of switchyard equipment and fault alarms: In case of power failure ,various alarm and indication systems in relays and control panel will not work, these systems provide visual or audible indications to the operator and indicate status of circuit breakers, isolators, earth switch etc.which help in assessment of fault and further action.
- Emergency lighting: Substations operate 24×7 , if there is power failure during the night in a substation, there will be some time delay in starting a DG set and putting it on load and this may cause delay in switching operations and be a cause of hazard for operational staffs.
In order to mitigate all these mentioned problems we require a stable, always available and reliable source of power which can be only met by D.C source. We call DC system of a substation as it’s heart as its importance in a substation is analogous to human heart .
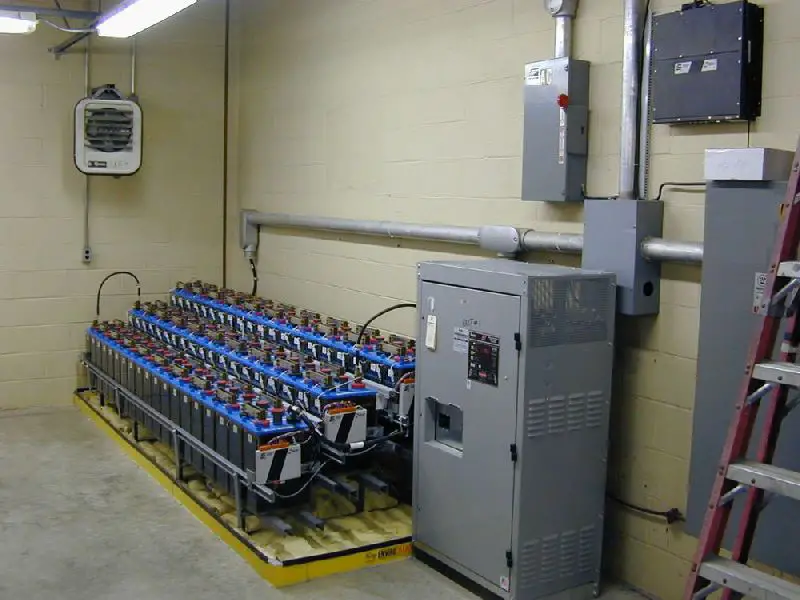

(DC battery bank)
DC (direct current) is used in substations for various purposes, primarily for control, protection, and communication systems. DC plays a vital role in ensuring the efficient and reliable operation of substations.
Here are some reasons why DC battery bank is used in substations:
Protection Systems: DC is extensively used in protection systems within substations. Protective relays, which are crucial for detecting faults and abnormalities in the power system, often rely on DC power. DC voltage sources are used to power these relays, ensuring their independence from the AC power system. This separation ensures that protection systems remain operational even during disturbances or faults in the AC system.
Control and Monitoring: Substations require accurate control and monitoring of various equipment and systems. DC is used for controlling switchgear, circuit breakers, and other devices within the substation. It provides stable and precise control signals, enabling efficient operation and coordination of substation equipment.
Alarm and Indication Systems: DC power is utilized to operate alarm and indication systems within protective relays. These systems provide visual or audible indications to the operator, alerting them to the occurrence of faults or abnormal conditions. The DC-powered indicators and alarms help the operator quickly identify the location and type of fault, facilitating prompt corrective actions.
Telecommunication and Signaling: Communication systems in substations play a vital role in transmitting information between different control and monitoring devices. DC power is used to supply energy to telecommunication equipment, such as data transmission devices, signaling equipment, and control panels. DC power ensures reliable and uninterrupted communication, enabling efficient monitoring and control of the substation.
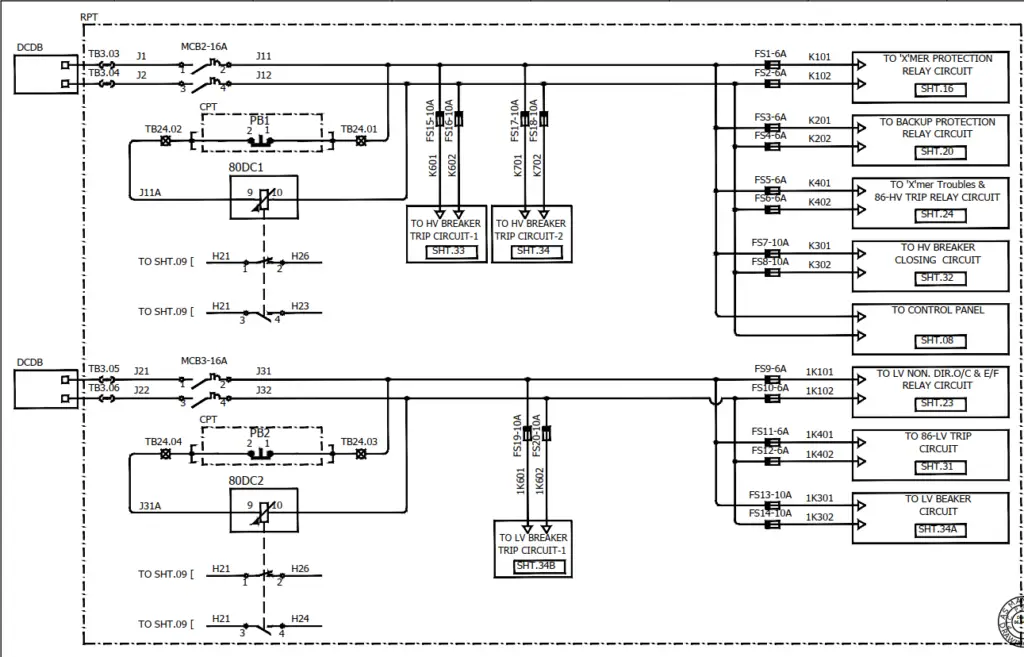
Please see the diagram below which is of DC distribution circuit in a control panel, you can see in the drawing that DC has been used in protection as well as opening/closing of breaker scheme.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on D.C. Battery Banks:
- What is a DC battery bank?
- A DC bank is a collection of interconnected batteries used to store direct current (DC) electrical energy. These banks are commonly employed in various applications, including backup power systems, renewable energy storage, and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS).
- What are the main components of a DC bank?
- A typical DC bank consists of individual batteries, interconnecting cables, fuses or circuit breakers, and sometimes a battery management system (BMS) for monitoring and control.
- How do I choose the right batteries for a DC bank?
- Battery selection depends on factors like the application, required capacity, discharge rate, maintenance needs, and environmental conditions. Common battery types include lead-acid, lithium-ion, and nickel-cadmium, each with its own characteristics.
- What is battery capacity, and how is it measured?
- Battery capacity refers to the amount of electrical energy a battery can store. It is typically measured in ampere-hours (Ah) for DC banks. For example, a 100Ah battery can deliver 1 ampere of current for 100 hours or 100 amperes for 1 hour.
- How are DC battery banks connected?
- Batteries in a DC bank are typically connected in series and/or parallel to achieve the desired voltage and capacity. Series connections increase voltage, while parallel connections increase capacity.
- How do I maintain a DC bank?
- Proper maintenance includes regular checks for corrosion, cleaning of terminals, equalizing charges (for some battery types), and monitoring the state of charge. The specific maintenance requirements depend on the battery type and manufacturer’s recommendations.
- What is a battery management system (BMS)?
- A battery management system is a device or software that monitors and manages the state of individual batteries within a bank. It helps optimize charging, prevent over-discharge, and improve overall battery performance.
- Can DC banks be dangerous?
- DC banks can be hazardous if not handled properly. They can deliver high currents and voltages, leading to electrical shocks, short circuits, and thermal hazards. Safety precautions and proper training are essential when working with DC battery banks.
- How long do DC batteries last?
- The lifespan of DC batteries varies depending on factors like the type of battery, usage patterns, maintenance, and environmental conditions. Typically, lead-acid batteries last around 3-5 years, while lithium-ion batteries can last longer, up to 10-15 years or more.
- How do I size a DC bank for my application?
- Sizing a DC bank involves calculating the energy consumption and the duration of backup power required. It’s important to choose a battery bank that can meet your specific needs without overloading or underutilizing the batteries.
- Can I connect different types of batteries in the same battery bank?
- It’s generally not recommended to mix different battery types in the same bank because they may have different charge and discharge characteristics, which can lead to performance issues and safety concerns.
When setting up a DC battery bank, it’s crucial to follow best practices, manufacturer recommendations, and safety guidelines to ensure reliable performance and safety in your specific application.